Damped Oscillations:
“The oscillations of a system in the
presence of some resistive forces are damped oscillation and an oscillating
system in which friction has an effect is a damped system.”
The oscillating system cannot be assumed to have a
fixed amplitude unless energy is provided to them. The resistive or damped
forces progressively reduce the amplitude of the oscillation. If a simple
harmonic motion is subjected to frictional forces, the amplitude of freely
oscillating objects progressively decreases. The friction not only affects the
amplitude but also slightly reduces the frequency. An oscillation that fades
away over time is called damped oscillation; The oscillations of a system in the
presence of some resistive forces are damped oscillations.
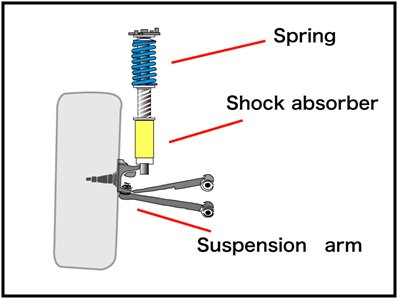
Working of Shock Absorbers:
The practical application of damped motion is shock absorbers in automobiles. A
shock absorber consists of a piston that moves through a liquid such as oil.
The upper part of the shock absorber is firmly connected to the body of the
automobile, when travels over a bump, the automobile may vibrate violently. The
shock absorbers dampen these vibrations and convert their mechanical energy
into the thermal energy of the oil.
No comments:
Post a Comment